In today’s fast-paced logistics world, many businesses look for ways to make their warehouses run smoother without spending a fortune. Warehouse automation on a budget is a smart choice for small to medium-sized companies that want to boost efficiency and cut costs over time. This guide focuses on using LiDAR and AGVs—two tools that work well together to automate material handling tasks. By combining budget warehouse automation LiDAR AGV setups, you can handle goods movement more reliably while keeping expenses in check.
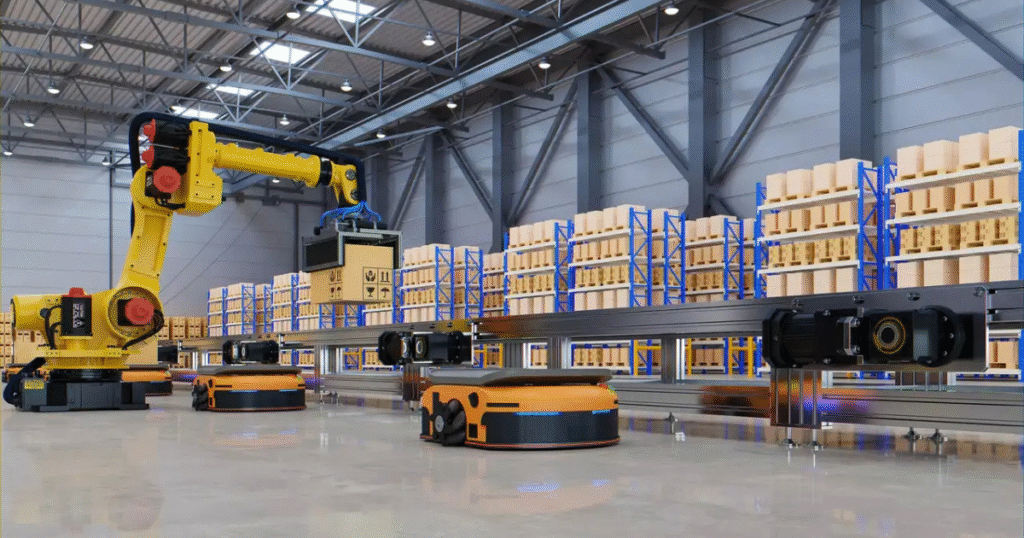
AGVs, or Automated Guided Vehicles, are self-driving carts or trucks that move items around the warehouse floor. LiDAR, which stands for Light Detection and Ranging, helps these vehicles see their surroundings by sending out laser pulses to map the area. Together, they create a system that’s accurate and safe for navigation, even in busy spaces. The good news is that you don’t need a huge investment to get started. Low-cost options have become more available, making it possible for smaller operations to adopt this tech.
Why go for budget warehouse automation LiDAR AGV? Labor shortages and rising wages make manual handling expensive. Automation reduces errors, speeds up processes, and improves safety by limiting human involvement in repetitive jobs. According to industry reports, warehouses using AGVs can see productivity gains of up to 30%, with payback periods as short as two years for basic setups. This guide will walk you through the basics, planning steps, implementation tips, and real-world advice to help you set up a system that fits your budget.
We’ll cover what AGVs and LiDAR are, their benefits, how to plan a low cost AGV implementation, details on warehouse LiDAR navigation, choosing equipment, setup processes, challenges, and future trends. By the end, you’ll have a clear path to automate your warehouse without breaking the bank.
What Are AGVs and LiDAR?
To understand budget warehouse automation LiDAR AGV, let’s start with the core parts. These technologies have been around for years but have gotten cheaper and easier to use.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
AGVs are battery-powered robots that transport goods in warehouses without a human driver. They follow set paths to move pallets, boxes, or carts from one spot to another. Basic AGVs use simple guides like magnetic tapes on the floor, while more advanced ones rely on sensors for freer movement.
There are several types of AGVs:
- Automated Guided Carts (AGCs): These are the simplest and often the cheapest. They handle light loads, like towing up to 2,200 pounds, and are great for sorting or cross-docking. Prices start at around $14,000 for basic models with magnetic navigation.
- Tugger AGVs: These pull trailers like a train, ideal for moving heavier loads over longer distances. A standard tugger with 2,000-pound capacity and magnetic navigation costs about $20,000.
- Forklift AGVs: They act like automated forklifts for pallet handling. These are pricier, starting at $60,000, but useful for stacking tasks.
- Unit Load Handlers: Focused on single items like totes, helping with receiving and shipping.
- Heavy Burden Carriers: For very heavy items, like steel coils, with costs up to $200,000 for high-end models.
AGVs work by sensing their environment and following instructions from a central software system. They integrate with your warehouse management setup via Wi-Fi, making them a key part of budget warehouse automation LiDAR AGV.
LiDAR Technology
LiDAR uses laser beams to measure distances and create 3D maps of the area. It sends out pulses of light and times how long they take to bounce back, calculating exact positions. This is the time-of-flight method, where distance equals speed of light times half the round-trip time.
In warehouses, LiDAR shines for indoor use where GPS doesn’t work. It builds point clouds—millions of data points per second—to map shelves, aisles, and obstacles. Accuracy can be as good as 2 cm, perfect for tight spaces. LiDAR helps AGVs avoid collisions and find the best paths, making warehouse LiDAR navigation reliable.
Costs for LiDAR sensors have dropped, with basic units for AGVs starting under $5,000. When paired with AGVs, it allows for natural navigation without fixed tracks, saving on installation.
Benefits of Budget Warehouse Automation with LiDAR and AGV
Switching to automation brings clear gains, especially when done on a budget. Here’s why budget warehouse automation LiDAR AGV makes sense.
First, it cuts labor costs. AGVs handle routine tasks like moving goods, freeing workers for higher-value jobs. Reports show reductions in labor expenses by up to 50% over time. With low cost AGV implementation, you start small and scale, avoiding big upfront hires.
Second, efficiency improves. AGVs run 24/7 without breaks, speeding up order fulfillment. LiDAR ensures precise navigation, reducing downtime from errors. In one study, warehouses saw throughput increases of 20-30%.
Safety is another big win. AGVs with LiDAR detect obstacles in real-time, stopping or rerouting to avoid accidents. This lowers injury risks and insurance costs.
Space use gets better too. AGVs need less room than manual forklifts, allowing narrower aisles and more storage. Flexibility is key—software updates let you change routes easily, adapting to business needs without major overhauls.
On the cost side, budget options like AGCs or basic tuggers pay back quickly. With Robot-as-a-Service (RaaS) models, you rent AGVs for as low as $50,000 entry level, spreading payments. Overall, these systems offer steady costs compared to variable human labor.
Planning Your Low Cost AGV Implementation
Getting started with low cost AGV implementation requires careful steps to stay within budget.
Start by assessing your needs. Look at your warehouse layout, load types, and daily movements. Calculate volumes for inbound, outbound, and internal shifts. Plan for future growth to avoid costly changes later.
Choose the right AGV type. For budgets, go with AGCs or tuggers using magnetic navigation—they’re cheaper than laser-based ones. Factor in payload, as higher capacities add cost.
Budget for extras like integration with existing systems, floor repairs, or conveyor upgrades. Use tools like free cost calculators to estimate total spend.
Pilot small. Test one or two AGVs in a section of your warehouse. This lets you spot issues without full commitment, saving money on fixes.
Involve your team early. Pick a “super user” with warehouse knowledge to oversee the rollout. Train responders for quick fixes to alarms, keeping downtime low.
Finally, track performance. Report downtime and adjust based on data to maximize ROI.
Warehouse LiDAR Navigation: How It Works
Warehouse LiDAR navigation is the brain behind safe and efficient AGV movement. Here’s a breakdown.
LiDAR sensors on AGVs emit lasers to scan the environment, creating 3D maps. In warehouses, this means mapping aisles, racks, and dynamic obstacles like workers or carts.
The system uses algorithms like Iterative Closest Points to match scans with stored maps, updating position 20 times per second. This allows AGVs to navigate narrow spaces with zero blind spots, using 360-degree views.
Pros include working in low light and high precision—down to centimeters. Cons: It can struggle with absorbent surfaces or fog, but warehouses are controlled, so this is rare.
For budget setups, pair LiDAR with basic AGVs for natural navigation, ditching expensive tracks. Sensors like the XT32 offer reliability in tough conditions, boosting safety.
Tips: Start with 2D LiDAR for simpler needs, upgrading to 3D for complex layouts. Integrate with software for path optimization.
Choosing the Right AGV for Your Budget
Picking an AGV means balancing features and cost. For budget warehouse automation LiDAR AGV, focus on essentials.
Consider payload first. Light loads? AGCs at $14,000. Heavier? Tuggers at $20,000.
Navigation type matters. Magnetic is low-cost but fixed; LiDAR adds flexibility for $5,000-10,000 more per unit.
Battery and charging: Gel batteries are cheap; online charging reduces downtime.
Look at add-ons sparingly—conveyors or lifts bump prices.
Vendors: Research for reliability. Start with RaaS to test without buying.
Examples: RoboCart is an ultra-low-cost demo using hub motors. Plastic cobot AGVs amortize quickly.
Integration and Setup
Setting up involves more than plugging in. For low cost AGV implementation, follow these steps.
Map your floor and install guides if needed. For LiDAR, create digital maps.
Connect to warehouse software for task assignment.
Test in phases: Simulate flows, then live runs.
Maintenance: Choose preventive plans to avoid high repair costs.
Involve all teams for smooth approval.
Case Studies and Examples
Many companies have succeeded with budget setups.
A small manufacturer used AGCs with LiDAR, cutting transport time by 40% at $30,000 total.
A logistics firm piloted tuggers, scaling to 10 units, saving on labor.
These show real ROI.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Challenges include high initial costs—solve with pilots and RaaS.
Integration issues: Plan data assumptions carefully.
Downtime: Assign responders.
Navigation errors: Use quality LiDAR.
Future Trends in Warehouse Automation
Looking ahead, costs will drop further. AI will enhance LiDAR for better prediction.
Hybrid AGV-AMR systems will offer more flexibility.
Sustainability: Electric AGVs reduce emissions.
Read more Interesting and informational Blogs Visit Our Website Lidarmos
Conclusion
Budget warehouse automation LiDAR AGV is achievable with planning. Start small, use low-cost options, and scale. This guide provides the tools to make your warehouse more efficient today.